Speed control of DC motor, dc motor speed control
Speed control of DC motor
speed control of DC series motor
Dc series motor speed can varies by changes in supply voltage and armature current
N = Back EMF / Flux
Back EMF = Supply voltage(V) – Armature voltage drop
N = Supply voltage – Armature voltage drop / Flux
from above equation Speed(N) is inversely proportional to Armature current and directly proportional to supply voltage . we can also change of speed by flux control because flux is inversely proportional to speed from above equation.
Methods which are used to vary in speed
1. Field diverter method
2. Armature diverter method
3. Field tapped control method
4. paralleling field winding method
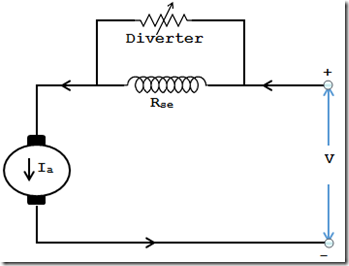
1. Field diverter method
it is common type of speed control of dc motor.
In this method a variable resistance (which called divert er)is connect across(parallel) the series field winding . In this type some series field current flow through diverter and less current flow through field winding which cause flux become less and motor will increase.
2. Armature diverter method
it is simple way of speed control of dc motor.
In this method a variable resistance (diverter) connect across(parallel) the armature.
 |
| Add caption |
In this method supply current will increase and flux will also increase from these cause motor speed become less. By this method we can reduced the speed of motor.
3. Field tapped control method
In this method provide tapping on field winding of DC series motor. this type according to no. of turn of field winding we can varies the speed of motor by change of taping position.
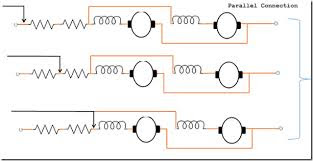
4. Paralleling field winding method
In this method field coils connect in parallel in each other which cause supply current divided in two part . from this method motor speed will increase
By using this method we can increase speed of DC series motor
Speed control of DC (shunt) motor
Back EMF = Flux * Z*N*P/60A
where Z is no. of conductor
N speed of motor in RPM
P is no. of poles in motor
A is no. of parallel path in Armature
N is directly proportional to EMF and inversely proportional to flux
Back EMF = V – Armature voltage drop
DC shunt motor speed can change by use of different method
A. Flux/Pole control
B. Armature current or Armature Resistance
C. Control of Supply voltage
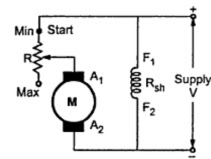
A. Flux/ Pole method
Flux / pole method
N is inversely proportional to flux
so we can change the speed of motor by change in flux . In this method a rheostats (Resistance) connected with field winding . which cause field current value become less and flux is also less so speed of motor increase.
By using this method motor speed only can be increase.
B. Armature control method
Speed is inversely proportional to Armature current
In this method a variable resistance connect with Armature series which cause Armature voltage drop increase hence speed become less.
So by using this method motor speed being less.
C. Voltage control
It is divided in two part
1. Multiple voltage control method
2. Ward Leonard method
1. Multiple voltage control method
In this method field winding connect to directly from line and given supply to Armature by help of varrier.
Supply voltage is directly proportional to motor Speed
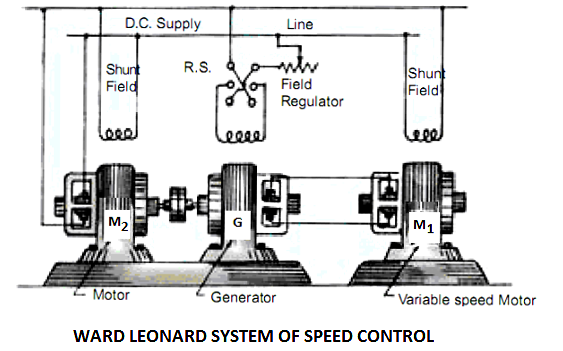
2. Ward Leonard method
In this method , motor and generator set are used to speed control of motor
Advantage of Ward Leonard system:
- . Uniform acceleration can be obtained.
- . Speed regulation is good
- . The wide range of speed from stand still to high speeds in either direction
- Rapid and instant reversal without excessively high armature current
- Starting without the necessary of series armature resistances.
- Steeples control from stand still to maximum speed in either direction.